Can Barefoot Shoes Help with Posture? What to Know

How Can Barefoot Shoes Help With Posture?
Excellent posture is not just about your physical appearance – it’s a cornerstone of your long-term health. And believe it or not, the secret to achieving better posture lies beneath your feet.
The footwear you choose can negatively impact your posture. The right type of shoes can help correct posture, providing comfort and better alignment for your body.
Let’s take a look at posture to see how the wrong footwear can cause problems, and how the right footwear could help your posture.
What Does Healthy Posture Look Like?
Proper posture means that your spine should be properly aligned when you stand. There are natural curves in your lower back, mid back, and neck, but excessive curvature in any of those places or flattening in any of those places can be problematic.
There are two types of posture: dynamic and static.
- Dynamic posture is how your body aligns during movement, for instance, walking, running, or bending over to pick up something.
- Static posture is how your body aligns when you are not moving, like sitting, standing, kneeling, or lying down.
How Bad Posture Affects the Body
Many people take good posture for granted until they notice negative effects.
Poor posture can have far-reaching consequences that affect our physical well-being. Here are some of the effects of bad posture to be mindful of:
- Misalignment of the musculoskeletal system
- Poor circulation
- Imbalances in the body
- Pain in the back or neck
- Increased number of injuries
- Stress on the ligaments and joints
- Lack of range of motion
- Decrease flexibility
- Tight muscles
- Weakened muscles
- Difficulty breathing
- Poor balance
- Decreased efficiency in daily life or athletic performance
What Causes Bad Posture?
Several factors contribute to poor posture. You may be doing some of these things and not even realize it.
Here are some common causes of poor posture:
- Prolonged periods of sitting: Having a sedentary lifestyle, you spend prolonged periods sitting or hunching over a desk, which can negatively affect posture over time.
- Not getting enough exercise can weaken the muscles that support your posture.
- Carrying excess body weight can strain the musculoskeletal system.
- Poor ergonomics in the workplace. This can commonly include improper desk setup, sitting for long periods of time, or incorrect positioning of computer screens.
- Sleeping position: Sleeping in positions that do not support proper spinal alignment.
- Stress, anxiety, and emotional tension leads to muscle tightness and increased muscle tension.
- Wearing improper footwear. Shoes can affect posture, disrupting your foot’s natural ability to offer a stable base for your body. At this point, you may be thinking, “what is improper footwear?”. We’ll review characteristics of shoes that can negatively affect posture, and what kind of footwear can help you have correct natural posture.
The Problem With “Normal” Shoes
Many “regular” shoes can actually cause posture problems.. Here’s how shoes can impact posture:
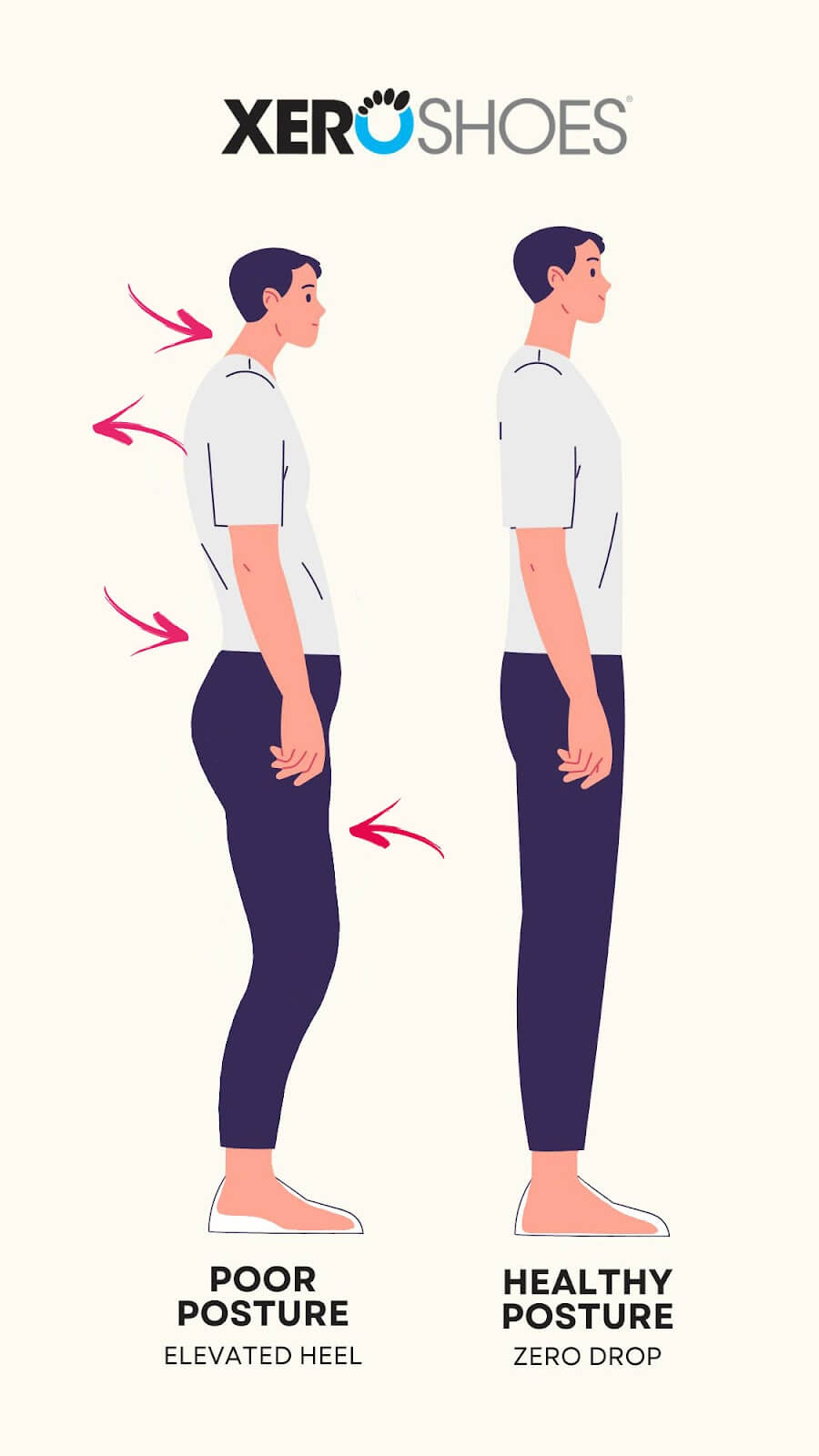
- Elevated heels of “normal shoes” move your center of mass forward. This alters the body’s natural alignment and can put extra pressure on the balls of the feet, ankles, hip, knees, or back to adjust for that change in center of mass.
- Padding that “normal shoes” typically have can negatively affect your posture. When foam cushioning wears out unevenly it can misalign your feet and ankles, which creates issues for your knees, hips and back.
- The narrow toe box of most conventional shoes can squeeze toes together and hinder natural toe splay. This can affect the overall stability of the feet, affecting the body’s balance and posture.
- Thick, Stiff Soles reduced sensory feedback affecting proprioception and balance. Your feet need to provide sensory information to your brain so you can move your body effectively and efficiently. When we lose touch with the ground, our body may lose its ability to make micro-adjustments that help us maintain proper dynamic posture.
How does this compare to barefoot shoes? They don’t have these issues.
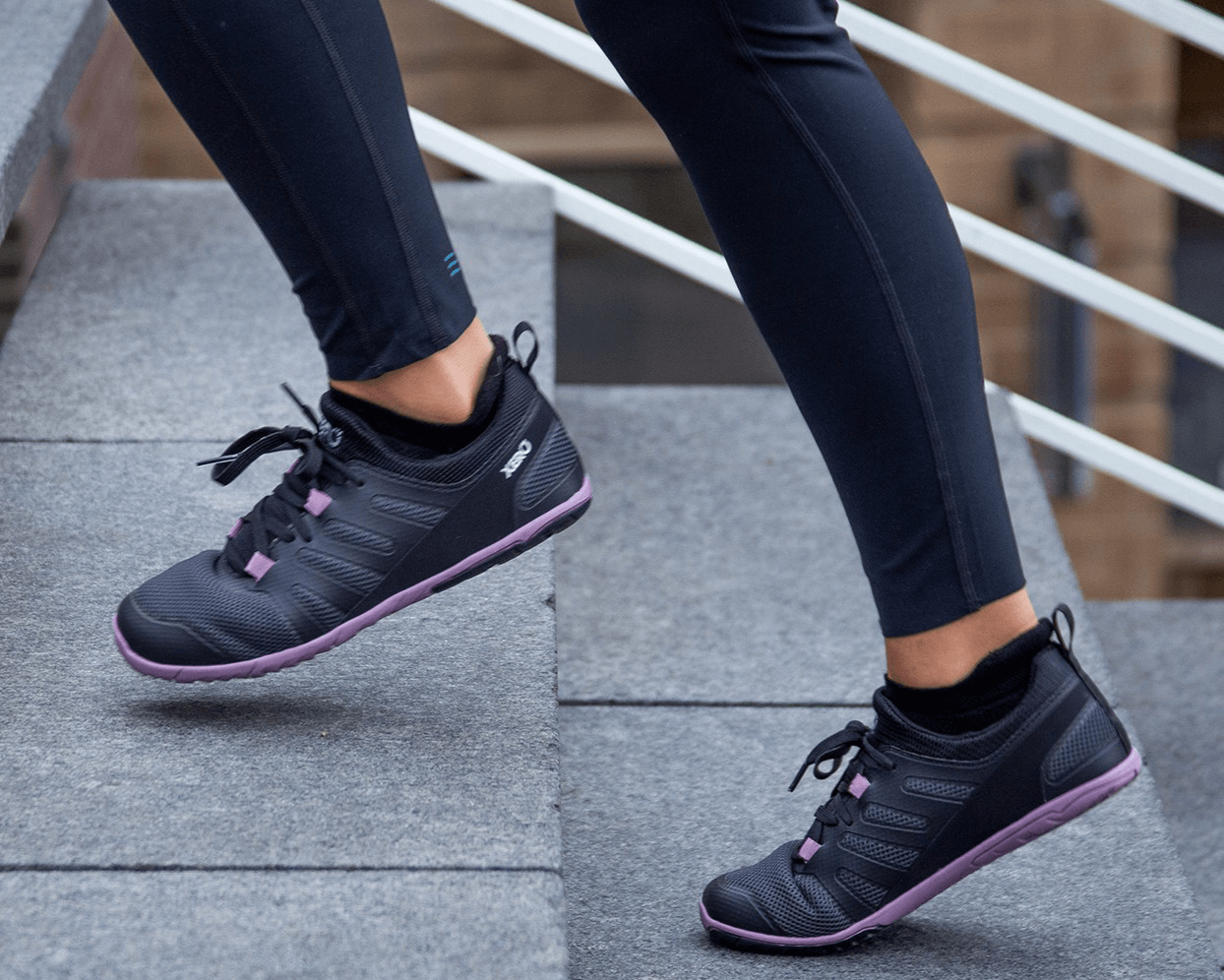
How Barefoot Shoes Can Help With Posture
Barefoot shoes are designed to help improve your posture.
While regular shoes can negatively impact posture, barefoot shoes mimic the feeling of being barefoot while providing the appropriate protection for your feet.
Barefoot shoes can help improve posture in a few ways:
- No Heel-Toe Drop: Most shoes have an elevated heel, which shifts your center of mass forward. This forces you to adjust with your ankles, knees, hips, and back. Where you will feel the stress depends on which one of these joints is least supported by your muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Barefoot (or “minimalist” ) shoes do not elevate the heel. This can keep the body in a neutral alignment and keeps the body weight centered over the feet.
- Thin (but protective), Flexible Soles: Barefoot shoes have a thin yet protective sole, so you can safely FEEL to ground and give your brain the feedback needed to make dynamic postural changes.
- Wider, Foot-Shaped Toe Box: In the same way spreading your fingers provides balance doing pushups, spreading your toes provides you with better balance while you stand, walk or run. Barefoot shoes feature a wider toe box, which gives your toes the freedom to spread out for better balance, stability, and posture.
Additional Tips to Improve Posture
Aside from wearing barefoot shoes, here are some other tips to improve your posture that you can begin including in your daily routine:
- Be Mindful: Being aware of your posture, whether sitting or standing, is essential. Take a moment to check in with your body throughout the day. Make sure your body is properly aligned.
- Take Regular Walking Breaks: If you have a sedentary desk job, it’s important to incorporate movement throughout the day. Set reminders to get up and take short walks, stretch, or do simple exercises.
- Vary your movements: By doing a variety of movements, you can help strengthen the muscles that support proper posture. This promotes muscle balance, flexibility, and core stability – all of which contribute to improved posture.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Carrying excess weight can place additional stress on your muscles, joints, and ligaments, affecting your posture. Strive to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
What people are saying about improved posture and barefoot shoes from Xero Shoes..
“I work as an ER charge nurse and I’m on my feet nonstop for 12 hour shifts. I recently purchased the prio shoes to use for work and they have been amazing. I was even told that I appear to be walking with better posture. Hopefully I can help others discover the benefits of these shoes.”
“I’m on my feet for 12+ hours and I needed shoes that give my feet plenty of support and that fit my foot. The barefoot feeling is ideal for my posture and for the anatomy of my foot. This is my second pair of Xero shoes and they did not disappoint!”
Making the Switch to Barefoot Shoes
If you’re ready for improved posture, it’s time to slip into a pair of barefoot shoes. Switching from a “normal” shoe to a barefoot shoe may be a bit of an adjustment, given the differences between the two.
The phrase “transition slowly” is a common recommendation people will tell you.
And while this isn’t wrong, transitioning to barefoot shoes is less about how quickly or slowly you make the change, and more about HOW you make the transition and not the length of time it takes.
FEEL What You’ve Been Missing; Natural Comfort, Posture, and Health
Barefoot footwear helps you FEEL the ground you’re walking on, and comes in many different styles of shoes, sandals and boots.
Not sure what type or style of shoe you want? Use this shoe finder quiz to find a few recommended shoes for you.
The content of this post does not constitute and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a physician or other qualified health provider with any questions or concerns you may have about your health or a medical condition.